Democrats will "fight like hell" against any efforts by Americans to stop teaching the CRT madness in public schools. That is because the bulk of democrat voters believe whiteness is an incurable disease, whites worship whiteness, and America is to be damned for its whiteness."Teach honest history"
When they teach that Obama is descended from slave owners I'll believe them.
When they teach that Kamala Harris is descended from slave owners I'll believe them.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Clarence Page: Who’s afraid of critical race theory? Those who don’t know what it is
- Thread starter annabenedetti
- Start date
Democrats will "fight like hell" against any efforts by Americans to stop teaching the CRT madness in public schools. That is because the bulk of democrat voters believe whiteness is an incurable disease, whites worship whiteness, and America is to be damned for its whiteness."Teach honest history"
When they teach that Obama is descended from slave owners I'll believe them.
When they teach that Kamala Harris is descended from slave owners I'll believe them.
The group insanity of CRT grows in strength as more and more weak-kneed Americans and corporations reluctantly support it for fear of persecution or ostracization if they don't.Teach white kids that they're "less than"
Teach white kids that they're "less than"
Idiots with lucrative teaching positions in secular universities continue to show their abject submission to group-think insanity by supporting racist CRT dogma.“Critical race theory,” or CRT, has become a trigger term for politicians, activists and media voices, particularly on the right wing where it’s competing with “cancel culture” on the hit parade of things we are all supposed to be angry about or afraid of — or both.
But the political allure of the term is understandable, considering how often it has been appearing in the fevered narratives of conservative media and Red State politicians. Texas, Tennessee, Oklahoma, Idaho, Arkansas and Arizona have either passed or are working on bills that would drop CRT or anything that looks like it from public schools curricula.
That’s a lot of agitation over an esoteric school of thought found mostly in graduate schools and law schools.
CRT has emerged gradually since the 1970s as an academic movement of civil rights scholars and activists to challenge mainstream liberal approaches to racial justice.
Among other pioneers of the CRT movement, legal scholar Kimberlé Crenshaw has called it an evolving practice that questions how race, as a social construct, perpetuates a caste system that relegates people of color to the bottom tiers.

Professor makes ‘average white’ student stand up in lecture, explains he has inherent 'benefit’ over black student no 'matter what he does' | Blaze Media
A professor at Penn State University recently made an "average white" student stand up in front of a 700-person lecture hall and explained that he has an inherent "benefit" over any black student, regardless of his behavior.What happened?Dr. Sam Richards, a popular sociology professor at the...
 www.theblaze.com
www.theblaze.com
ok doser
lifeguard at the cement pond
Sociology professorIdiots with lucrative teaching positions in secular universities continue to show their abject submission to group-think insanity by supporting racist CRT dogma.
A professor at Penn State University recently made an "average white" student stand up in front of a 700-person lecture hall and explained that he has an inherent "benefit" over any black student, regardless of his behavior.
Professor makes ‘average white’ student stand up in lecture, explains he has inherent 'benefit’ over black student no 'matter what he does' | Blaze Media
A professor at Penn State University recently made an "average white" student stand up in front of a 700-person lecture hall and explained that he has an inherent "benefit" over any black student, regardless of his behavior.What happened?Dr. Sam Richards, a popular sociology professor at the...www.theblaze.com
nuff said
Hundreds of anti-American leftist racist activists insist they will keep teaching CRT to their students even if the racist doctrine is outlawed.Sociology professor
nuff said
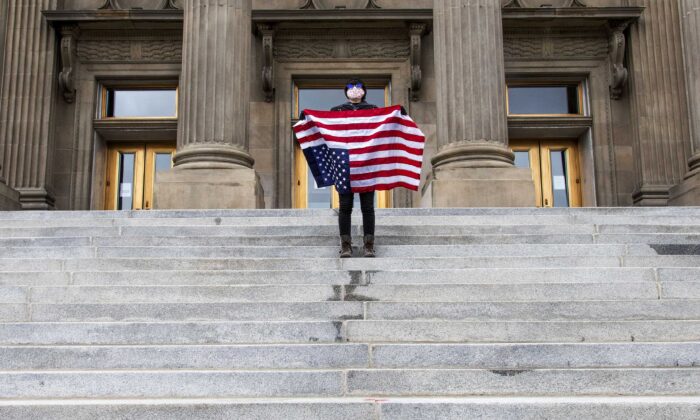

Over 5,000 Sign Pledge to Continue Teaching Critical Race Theory Even if Outlawed
The petition requires one to declare their role as a “teacher, principal, librarian, etc.” but their roles are not displayed under their names and comments.
What kind of definition can be put on a theory which insists whites are evil and racist and need to be humbled? Poppycock comes to mind as a good definition of the lying leftist junk theory.Critical Race Theory has become the new front in the culture wars. Both proponents and opponents of it seem to have the same goal—to stamp out racism in the U.S. So why is it so divisive? Part of the answer lies in how people are defining CRT:
Radicals in the democrat party do not hide their contempt for America, for cops, for white people, for conservatives, for republicans, for Bible-believing Christians, for patriotism, for right interpretations of the Constitution, and so forth. Why Americans have allowed these hateful radicals to seize power in the US is a mystery.“Critical race theory,” or CRT, has become a trigger term for politicians, activists and media voices, particularly on the right wing where it’s competing with “cancel culture” on the hit parade of things we are all supposed to be angry about or afraid of — or both.
But the political allure of the term is understandable, considering how often it has been appearing in the fevered narratives of conservative media and Red State politicians. Texas, Tennessee, Oklahoma, Idaho, Arkansas and Arizona have either passed or are working on bills that would drop CRT or anything that looks like it from public schools curricula.
That’s a lot of agitation over an esoteric school of thought found mostly in graduate schools and law schools.
CRT has emerged gradually since the 1970s as an academic movement of civil rights scholars and activists to challenge mainstream liberal approaches to racial justice.
Among other pioneers of the CRT movement, legal scholar Kimberlé Crenshaw has called it an evolving practice that questions how race, as a social construct, perpetuates a caste system that relegates people of color to the bottom tiers.
Joy Reid Calls Republicans Racist Terrorists, Says They Want Another 9/11 But for Black People - LifeNews.com
In the almost-year since MSNBC’s The ReidOut was born, NewsBusters readers have seen host Joy Reid and the show foment dangerous and incendiary rhetoric against conservatives and Republicans. Wednesday’s show was one of the worst as Reid and a cast of characters painted right-leaning Americans...
www.lifenews.com
"We hope you die!" Is that what racist and liberal school officials really want to say to white parents who do not want schools telling white kids that they are racist because they are white?“Critical race theory,” or CRT, has become a trigger term for politicians, activists and media voices, particularly on the right wing where it’s competing with “cancel culture” on the hit parade of things we are all supposed to be angry about or afraid of — or both.
But the political allure of the term is understandable, considering how often it has been appearing in the fevered narratives of conservative media and Red State politicians. Texas, Tennessee, Oklahoma, Idaho, Arkansas and Arizona have either passed or are working on bills that would drop CRT or anything that looks like it from public schools curricula.
That’s a lot of agitation over an esoteric school of thought found mostly in graduate schools and law schools.
CRT has emerged gradually since the 1970s as an academic movement of civil rights scholars and activists to challenge mainstream liberal approaches to racial justice.
Among other pioneers of the CRT movement, legal scholar Kimberlé Crenshaw has called it an evolving practice that questions how race, as a social construct, perpetuates a caste system that relegates people of color to the bottom tiers.
'Let them die!': PTA, NAACP official demonizes parents against critical race theory | Blaze Media
Crowds gathered outside the Luther Jackson Middle School in Virginia, where concerned parents were rallying against critical race theory being taught to students in Fairfax County Public Schools. During Thursday's "Stop CRT Rally," a PTA and NAACP official spewed rhetoric against the parents...
 www.theblaze.com
www.theblaze.com
ok doser
lifeguard at the cement pond
Here - allow me to present Thomas Sowell, one of the smartest people you're likely to encounter.It's basically non-whitewashed U.S. History. You know, adding in the parts that have been conveniently left out ...
Learn
CRT is thinly veiled sedition and it is overtly racist and transparently false. The fact of the matter is that less than five percent of black slaves ever stepped foot in the United States and the country was still quite young when it faught a civil war that ended the practice. Both a practice and a war that the left was on the wrong side of, I might add. It was southern Democrats that kept racism alive after the civil war and its leftist Democrats that are keeping it alive today.“Critical race theory,” or CRT, has become a trigger term for politicians, activists and media voices, particularly on the right wing where it’s competing with “cancel culture” on the hit parade of things we are all supposed to be angry about or afraid of — or both.
But the political allure of the term is understandable, considering how often it has been appearing in the fevered narratives of conservative media and Red State politicians. Texas, Tennessee, Oklahoma, Idaho, Arkansas and Arizona have either passed or are working on bills that would drop CRT or anything that looks like it from public schools curricula.
That’s a lot of agitation over an esoteric school of thought found mostly in graduate schools and law schools.
CRT has emerged gradually since the 1970s as an academic movement of civil rights scholars and activists to challenge mainstream liberal approaches to racial justice.
Among other pioneers of the CRT movement, legal scholar Kimberlé Crenshaw has called it an evolving practice that questions how race, as a social construct, perpetuates a caste system that relegates people of color to the bottom tiers.
I am not racist by virtue of the color of my skin and I will physically hit anyone in the mouth that says otherwise to my face. I will not reason with them, I will not even speak to them. They are well beyond the point that any rational discourse can remedy. If they are within range, the cost of calling me a racist is facial blood flow and I am not kidding.
You communists want to start a race war? I'm ready! Let's get it on. I'll kill all the communists I can, regardless of the color of their skin. Don't bitch when you get what you've asked for.
Clete
ok doser
lifeguard at the cement pond
My favorite meme from last month (which I can't find :sozo2: ) went something like:CRT is thinly veiled sedition and it is overtly racist and transparently false. The fact of the matter is that less than five percent of black slaves ever stepped foot in the United States and the country was still quite young when it faught a civil war that ended the practice. Both a practice and a war that the left was on the wrong side of, I might add. It was southern Democrats that kept racism alive after the civil war and its leftist Democrats that are keeping it alive today.
Juneteenth - celebrating the day Republicans told Democrats they couldn't own slaves anymore
ok doser
lifeguard at the cement pond
I have to admit....Using the confusion of a civil war to camouflage "settling accounts" is an idea which never gets old.You communists want to start a race war? I'm ready! Let's get it on. I'll kill all the communists I can, regardless of the color of their skin. Don't bitch when you get what you've asked for.
Clete
Speaking of CRT inciting hate crimes, someone needs to call up Merrick Magoo Garland and tell him the problem in America is not so much white hate crimes against blacks as it is black hate crimes against whites.I don't watch the news.
You made a bold statement:
"CRT is a 'philosophy.' That philosophy is pointed to education/re-education of American pupils to get them to think about 'race equity, race inequity, and race privilege.' More often than not, such 'education' is causing race-hate crimes"
but you have nothing to back it up. So, it's your opinion then.
By "that particular," do you mean being Black?
What you simply refuse to get from it: That an Alabama lawmaker wants to ban what he doesn't know anything about. Doesn't engender much trust in his ability as a lawmaker, does it?
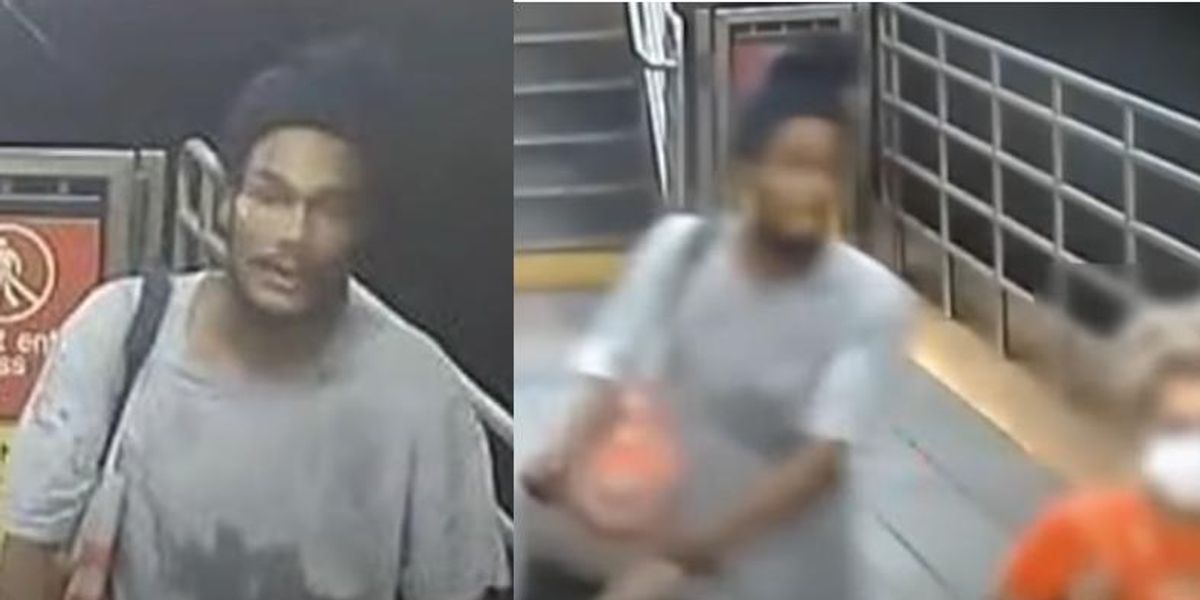

Goon slugs grandmother while she was listening to the rosary in unprovoked Grand Central subway attack | Blaze Media
Video shows an unprovoked attack on a 60-year-old woman at the Grand Central subway station in New York City. The woman was slugged in the head and suffered injuries that will keep her out of work for weeks. Luzby Gallego was walking on the 7 train platform at Grand Central Station on the night...
 www.theblaze.com
www.theblaze.com
Arthur Brain
Well-known member
If you think anna's a communist then you're clueless. If you think she wants a race war then you're clueless. If you think that it's democrats and "leftists" that kept racism alive and are keeping it alive today then you're clueless. White supremacist nutball outfits are far right for starters. You'd kill all the "communists" you could would you? Seriously pathetic.CRT is thinly veiled sedition and it is overtly racist and transparently false. The fact of the matter is that less than five percent of black slaves ever stepped foot in the United States and the country was still quite young when it faught a civil war that ended the practice. Both a practice and a war that the left was on the wrong side of, I might add. It was southern Democrats that kept racism alive after the civil war and its leftist Democrats that are keeping it alive today.
I am not racist by virtue of the color of my skin and I will physically hit anyone in the mouth that says otherwise to my face. I will not reason with them, I will not even speak to them. They are well beyond the point that any rational discourse can remedy. If they are within range, the cost of calling me a racist is facial blood flow and I am not kidding.
You communists want to start a race war? I'm ready! Let's get it on. I'll kill all the communists I can, regardless of the color of their skin. Don't bitch when you get what you've asked for.
Clete
It is not white supremacists who are killing thousands of Americans each year, but black supremacist lives matter gangsters who are murdering so many.If you think anna's a communist then you're clueless. If you think she wants a race war then you're clueless. If you think that it's democrats and "leftists" that kept racism alive and are keeping it alive today then you're clueless. White supremacist nutball outfits are far right for starters. You'd kill all the "communists" you could would you? Seriously pathetic.


